What Is Google Cache? Everything Website Owners Need to Know

You’re probably aware that Google uses crawler bots to crawl websites and scan content. But did you know that Google does more than just crawl websites? However, you can’t help wondering, somewhere in the back of your mind, what exactly the Google cache is?
When you visit a website, your browser downloads a copy of the site and saves it to your computer’s hard drive. When you’re finished, the next time you visit the same website, it will load faster. It stores data such as images, movies, scripts, and other technical data, resulting in a faster loading time. A cache is essentially a collection of items stored in a secret location. Google Cache is simply a raw HTML backup of a page’s content or a copy of a page kept by Google as a backup.
What Is Google Cache?
All of the websites we can access are hosted on remote servers. Googlebot must visit websites, crawl through their content, and index them in order to provide search results to users.
Google, on the other hand, does something else. It takes a snapshot of every webpage and saves it as a backup in case the live page is unavailable for any of the reasons listed above. Google Cache is a unified database that stores millions of sites as a backup.
The method improved the user experience. For example, if any of the search results pique your interest but are not currently available (due to being deleted, offline, or otherwise), you can access the web page via Google Cache.
Google Cache is updated on a regular basis by Google. Unless Google updates the snapshot of the website, modifications made by designers will not appear in the Google Cache.
Why Google Cache Is Important
Websites are constantly evolving. The majority of the changes are the result of website owners’ marketing efforts to improve the site’s user experience and relevance to the target audience.
However, there are other culprits, such as hackers who intentionally tamper with the information on websites or unforeseeable circumstances that result in fatal data errors.
Here are some of the reasons why it is important to cache websites, Deleted Webpages, Improving Page Loading Speed, Convenient Backup.
How To Access Cached Versions Of A Website
Even if you’ve seen cached sites from the search results page before, you should read this because Google changed the way to find a cached link in early 2021.
To begin, use Google to find the page you want to see. In the search results, you should see three vertical dots next to the URL of the page. When you click them, a pop-up window labelled “About this result” should appear:
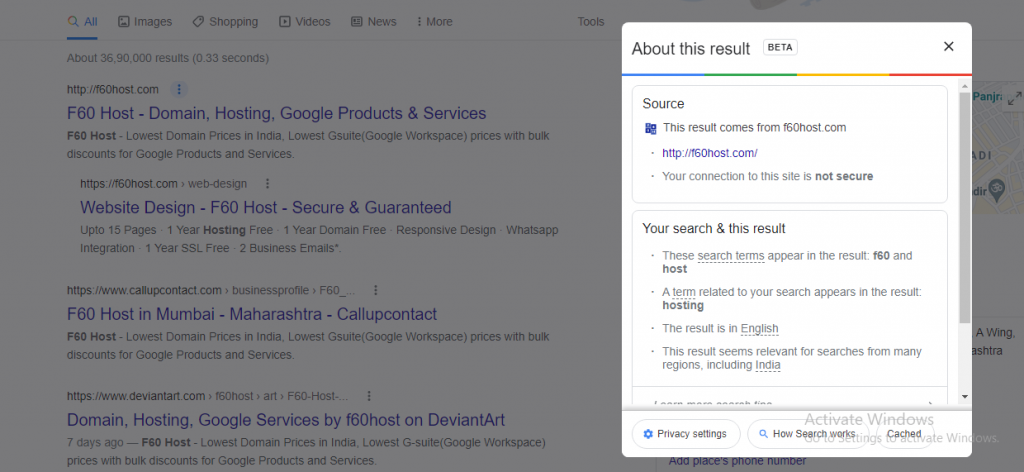
There’s a Cached button at the bottom right of the pop-up. To view the cached page, click it.
It’s possible that you won’t see a Cached button in some cases. That could indicate that the page hasn’t been cached; we’ll go over what that means in a moment.
However, if you are using a mobile device, you will not see the button for any page. In that case, keep reading to discover another way to view a cached page.
Use Google Chrome Browser or Google Chrome plugins
You can access Google Cache directly from the Google Chrome web browser. Open Google Chrome and type the following address cache:www.websitename.com. Or you can use Google Chrome plugins such as Web Cache Viewer, which can enable you to access cached versions of web pages on the go.
This action enables you to directly access cached versions of your favorite websites or your own website without having to go through search results.
Reasons To Use Google Cache as a Website Owner
However, Google Cache is difficult to beat in terms of speed and ease of use. As a result, it is a useful tool for monitoring specific aspects of your web pages.
Here are five ways you can use Google Cache as a site owner.
- Check for Duplicate Content
- Verify That Google Respects Your Canonical Tags
- Check to See If Your Marketing Efforts Have Been Crawled
- Monitor Changes to Competitor Websites
- Get the Most Recent Version of Your Website
More Information
For more information about Google G Suite/Workspace domains, Server, Hosting, check out these F60 Host resources:



