Shared Hosting Page Load Metrics You Need To Watch

Page Load Metrics To Keep An Eye On In Shared Hosting
Is your website frustratingly sluggish to load? It’s simple to add new features and plugins to your website, so it’s understandable if your page load times begin to suffer. We’ll show you the most crucial page load metrics to start tracking in this article. This will allow you to keep sites hosted on a Shared Hosting plan responsive and speedy!
Find out how to…
- Check your page load time
- Find out which files are tanking your load time
- Take meaningful actions to optimize
Fully Loaded Page Time
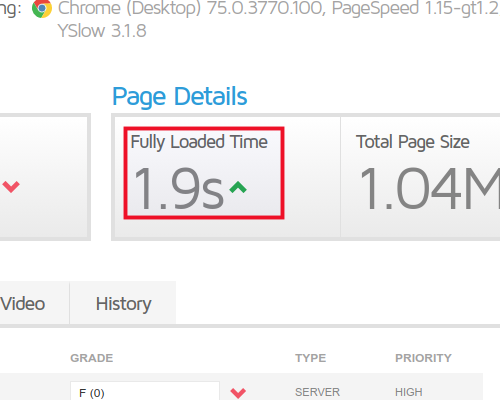
The fully loaded page time of your site is the number of seconds it took to render a page completely. This is the most crucial value, and it should be as low as possible. In general, less than 4 seconds is regarded as good, but for a fully loaded website, you should aim for around 2 seconds. you can check your page speed on PageSpeed Insights
Waterfall
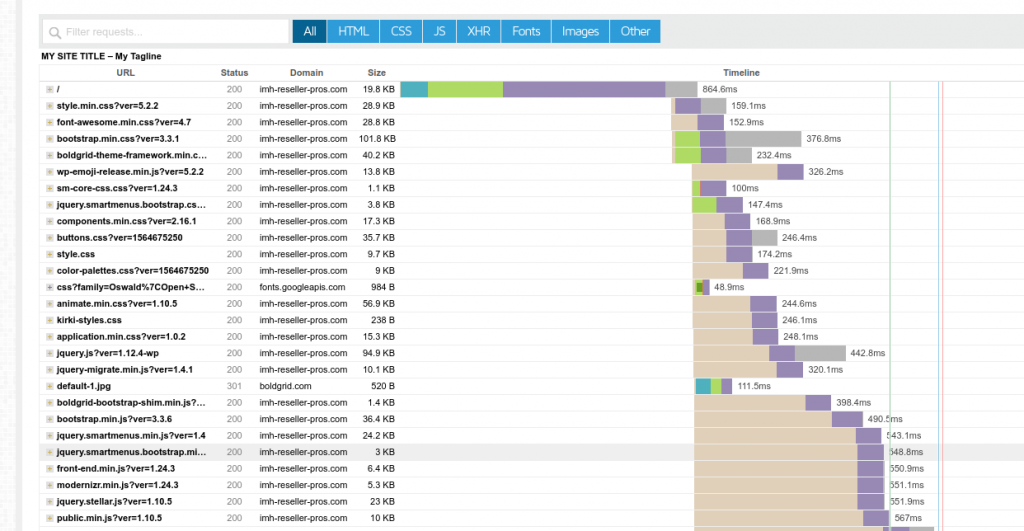
If a page takes more than 4 seconds to fully load, you’ll need to start looking into the problem. A “waterfall” function will show you every file your website uses during the load time, as well as how long each file took to load. This information is quite useful in determining which file is the slowest.
Take Action – Notable Warnings And How To Fix Them
You’ve already made significant progress toward speeding up your slow website. You may now take raw data and put it to use. We’ll go over some of the most common warnings you might see in your site report (at least on GTMetrix) and what you can do about them.
Leverage Browser Caching
It may appear that utilizing browser caching is difficult, but it is fairly simple. When you enable browser caching, you’re allowing your pages to be saved in a user’s browser when they visit your website for the first time. This means the page will load faster when they return. All kinds of page resources (even sections of a page) can be saved, making the entire site load faster.
Good news for WordPress users: using a plugin like WP Super Cache, you can easily optimize your site for browser caching. If you have a custom-built site, we recommend contacting our live support staff, as well as your developer or IT person, for information on how caching can help you optimize it.
Defer JavaScript Parsing
Deferring JavaScript parsing once more may appear to be a difficult task, but it only means that JavaScript files should be loaded after the main page content. In most cases, JavaScript adds extra functionality to your site for design or usability. It can also be used to gather information about how visitors interact with your site. However, because these scripts might increase the time it takes for your site to load, they should be delayed until after the primary content of your page has loaded. While the JavaScript loads in the background, your visitors will have something to look at.



