What is DNS and How DNS works?

What is DNS?
Domain Name System (DNS) services are what DNS stands for. When we visit a website, we use this service to find the server that hosts the domain’s website. We normally type in a domain name like www.google.com into our browser when we go online. This is preferable to trying to recall an IP address associated with a Google server.
Behind the scenes, a conversion of www.google.com to 172.217.12.46 is performed utilizing this service. The IP address identifies a server’s location on the Internet. An inquiry is a name for this conversion procedure. This is an important aspect of how devices communicate with one another over the internet. Let’s have a look at how this query works to better grasp the query procedure.
DNS Process Steps
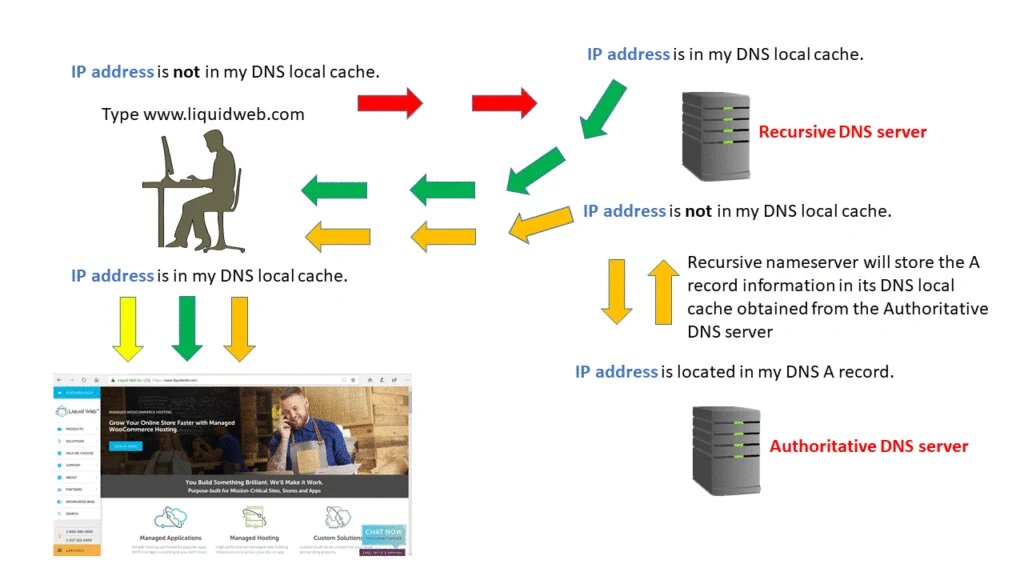
Step 1 – Requesting Website Information
Let’s go to a website by typing the domain name into the address bar of a web browser. The hostname, such as www.liquidweb.com, will be resolved by our computer. Our computer will then search its local cache for the IP address associated with the domain name. This cache keeps track of the data that our computer has lately saved. The webpage will be displayed if it is available locally. If our computer doesn’t have the information, it will run a DNS query to get it.
Step 2: Contact the Recursive DNS Servers
It will query another server if the information is not in your computer’s local cache. Recursive servers, like your computer, have a local cache. Because many ISPs utilize the same recursive DNS servers, a common domain name may already be cached. The query will finish here if the domain is cached, and the user will see the webpage.
Step 3: Query the Authoritative DNS Servers
If a recursive DNS server or servers can’t find what they’re looking for in their cache memory, they look elsewhere. The query then moves up the authoritative server chain. The search will go on until a nameserver for the domain is found. These authoritative name servers are in charge of maintaining these records for their domain names.
Step 4: Access the DNS Record
To find the IP address for liquidweb.com, we’ll look up the address record on the authoritative name server (A record). The A record for liquidweb.com is accessed by a recursive DNS server from the authoritative name servers. The record is then saved in its local cache. The recursive server will have the answer if another query asks for the A record for liquidweb.com. A time-to-live value is assigned to all records, and it indicates when the record will expire. The recursive DNS server will request an updated copy of the records after some time has passed.
Step 5: Final DNS Step
The information is stored on the Recursive server, which returns the A record to your computer. The record is then saved in our computer’s local cache. It obtains our IP address from the record and sends it to our browser. The website will be displayed after the web browser connects to the webserver connected with the A records IP.
The full lookup operation takes milliseconds to complete from start to finish. Let’s break down the components that make up the lookup process for a better understanding.
How Does DNS Works?
DNS resolution is the process of translating a hostname (for example, www.example.com) into a computer-friendly IP address (such as 192.168.1.1). Each device on the Internet is assigned an IP address, which is required to locate the proper Internet device, much like a street address is required to locate a certain residence. When a user requests a webpage, a translation must take place between the user’s input (example.com) and the machine-friendly address required to locate the example.com webpage.
To comprehend the resolution process, it’s necessary to first learn about the many hardware components that a query must transit through. Apart from the initial request, the DNS lookup occurs “behind the scenes” in the web browser and requires no input from the user’s computer.