What is Multicloud: Why Use Multicloud?
In general, the term “multicloud” refers to the use of cloud services from two or more different public cloud providers. It frequently also refers to unique architectural arrangements where an app makes use of the same service model from a number of different cloud service providers, sometimes even on-premises data centers and colocation facilities.

As part of a multi-cloud strategy, a business may leverage two or more cloud computing platforms to achieve a range of goals. Utilizing services from various heterogeneous cloud service providers, such as AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, as well as specialized PaaS, IaaS, or SaaS providers, is known as multicloud. Hybrid cloud, which combines the use of private cloud environments and public cloud environments, is not the same as multicloud.
The use of multicloud as an architectural option is flexible. The most obvious one is recovery from disasters. Although cloud vendors provide a range of alternatives and SLAs (service-level agreements) for redundancy to assure uptime and backups to maintain data integrity, both of these depend on the assumption that the vendor’s entire infrastructure does not fail at once.
What are Single-Cloud and Multi-Cloud Storage Systems?
The number of cloud service providers an organisation partners with determines whether it uses a single cloud or multiple clouds. One cloud storage provider handles all of an organization’s cloud storage requirements and capabilities when it employs a single-cloud strategy.. a company that offers cloud services. Public clouds are those that are shared by many users.
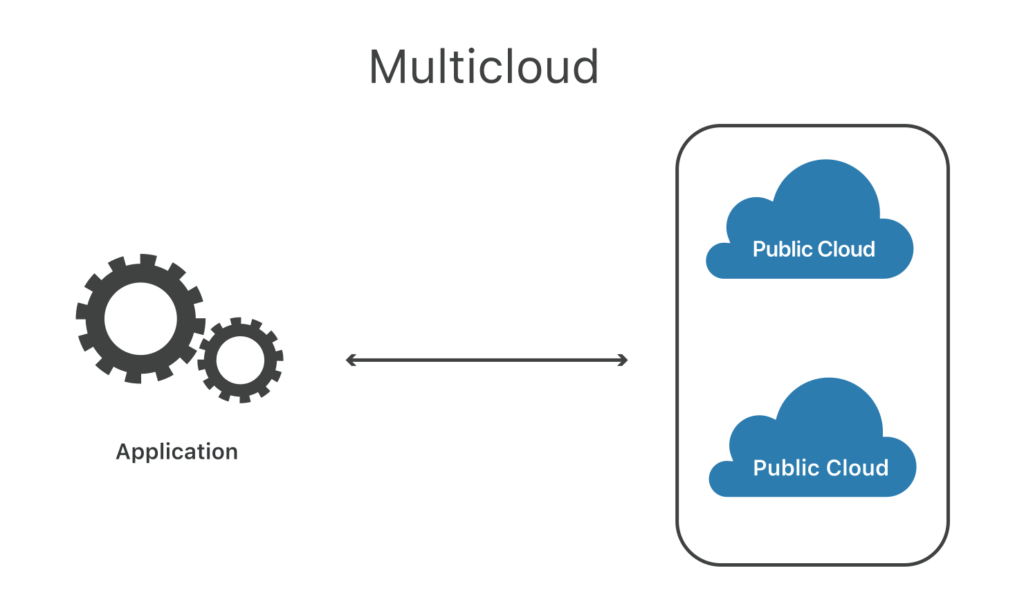
Multi-cloud means multiple public clouds. A company that uses many public clouds from different cloud providers has a multi-cloud arrangement. When a company employs many cloud providers, it avoids relying just on one for cloud hosting, storage, and the full stack of applications.
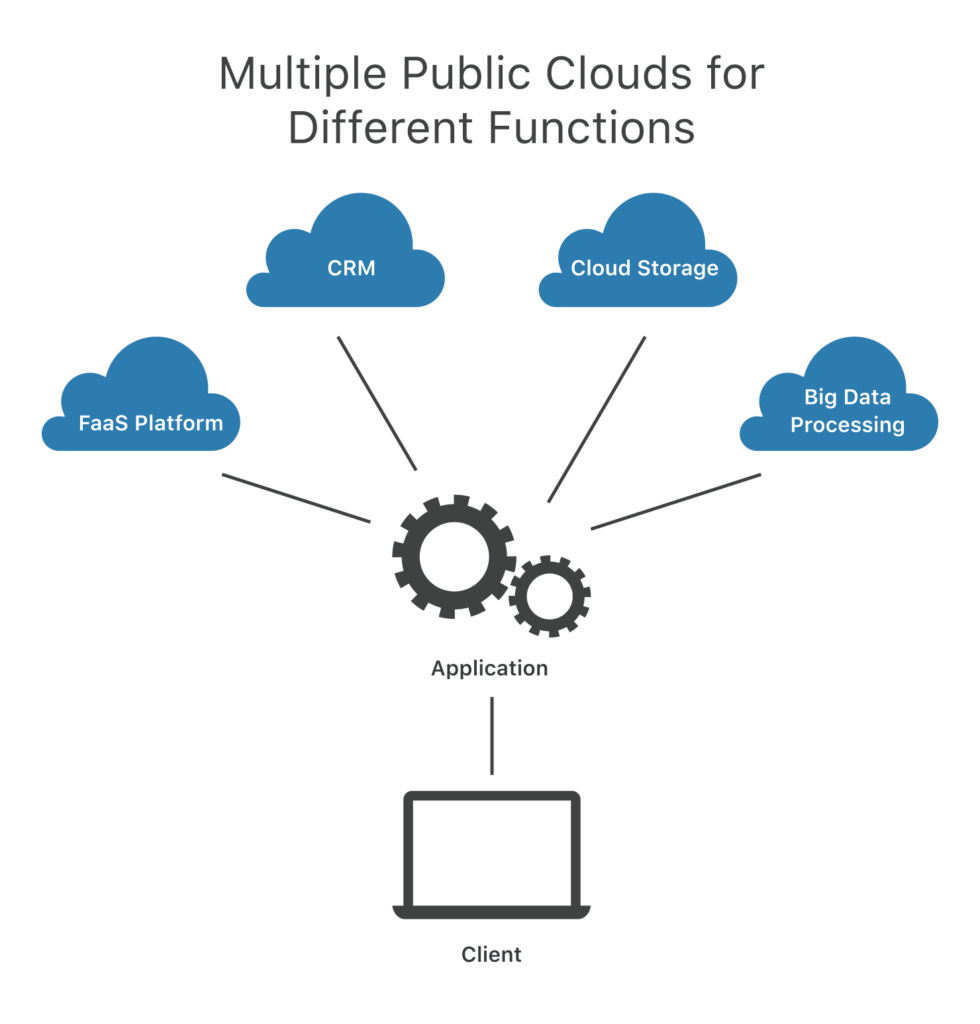
Multicloud deployments have a number of uses. A multicloud deployment can employ separate PaaS (platform-as-a-service), SaaS (software-as-a-service), and IaaS (infrastructure-as-a-service) vendors, or it can use several IaaS (infrastructure-as-a-service) vendors. Multicloud might include various cloud vendors for various services, or it can be used merely for redundancy and system backup.
The majority of firms that go to the cloud will eventually implement several clouds.Even accidentally, shadow IT can lead to a multicloud implementation (see below).
What Advantages do multicloud Deployments Offer?
The key benefit of multicloud is that businesses and application developers can select components from many vendors and employ the ones that are most suited for their intended use. In contrast to a table d’hôte, multicloud is more à la carte.
However, this advantage might be contingent on a microservices architecture. For instance, a company might host its live e-commerce site on AWS with its customer database and product catalogue, and then host a replica on Google Cloud that generates personalised content and offers based on user interactions.
The services an organisation choose will depend on its personnel’s skill sets and current IT infrastructure. Utilising some Microsoft Azure services, for instance, may be advantageous for companies who have an excessive reliance on the Windows ecosystem, whereas the same company may use Google Cloud for machine learning. For web services with a public face, consider analytics and learning or Amazon.
The reduction of concentration risk and data sovereignty are two further benefits of multicloud. People in Europe are getting more and more worried about this.
Low latency access to an organisation’s application is another benefit of multicloud. Organizations have observed capacity restrictions across a number of clouds, with low or even no capacity, as cloud demand has grown. The ideal cloud provider for a company could not yet have data centres operational in an area close to their clients.
If an application has been particularly designed to run across several clouds, multicloud enables an organisation to mix and match infrastructure in order to support it. For instance, a particular cloud service can exist but be located in a place that is too far away geographically to give adequate application performance, making a different cloud provider the wiser choice.
What distinguishes multicloud from hybrid cloud?
Both a Multicloud and a hybrid cloud can exist simultaneously, however these phrases refer to two different concepts.
The term “hybrid cloud” refers to the blending of two or more different types of infrastructure, including at least one public cloud and either a private cloud, an on-premise data centre, or both. Multicloud is the term for the deployment of numerous different public clouds; it can also refer to a private cloud.
What are the Pros and Cons of Using Multicloud Strategy?
Pros:
- Reliability and/or redundancy: An organisation can avoid placing all of their eggs in one basket by employing a multicloud deployment. If one cloud fails, users will still be able to access some functionality from the other deployed clouds.. A public cloud can also be used as a backup for another cloud.
- Reduced vendor lock-in: Moving to the cloud necessitates relying on outside cloud providers, and when businesses utilise these vendors more frequently, it may be challenging to switch to another vendor. A multicloud model, however, disperses systems and storage across various vendors. It is easier to transition from using one of these suppliers because the vast majority of the infrastructure remains in place during the transfer.
- Potential cost savings: Businesses have the freedom to select the most economical services if they do not commit to employing a single cloud vendor for all of their infrastructure requirements from different vendors.
Cons:
- Complexity of management Interacting with numerous different providers, each with their own practises and technological capabilities, is required for a multicloud deployment. Additionally, it becomes more challenging to have complete visibility into the technology stack as activities and data are spread across multiple clouds.
- Increased latency: Depending on how closely the clouds are connected, latency may be introduced if services from different clouds must communicate in order to perform user requests how far apart the data centres are geographically and how frequently different clouds must communicate with one another.
- Greater attack surface: There are probably more vulnerabilities the more software and hardware are combined.
- Performance and reliability: Load balancing between various clouds can be challenging, especially if the data centres are spread out geographically. (Cloudflare Load Balancing is able to evenly distribute loads between clouds.)
What does multicloud architecture look like with Cloudflare?
Cloudflare sits between end users and cloud infrastructure. Any cloud provider, or a number of cloud providers, can be integrated with, secured, and have traffic accelerated.
The traffic between end users and the origin cloud infrastructure can incorporate a number of Cloudflare services.Shadow IT can find its way into application architecture tooEmployees may integrate cloud services into a company’s technology stack without official authority, either as a workaround or out of necessity. In order to further reduce latency, we offer multi-cloud load balancing, which divides traffic among many clouds, and CDN caching. For increased security, our Web Application Firewall (WAF) prevents harmful traffic.
What is shadow IT?
Inadvertent multi-cloud deployments may occur as a result of shadow IT. Internal teams sometimes utilise software or set up technological systems without receiving formal approval from the larger organization or oversight. This is known as “Shadow IT.” A straightforward illustration would be if staff members of a corporation used a chat app to discuss work-related matters but the app was not authorized or controlled by the organisation.
Shadow IT is also able to penetrate application architecture. Employees may integrate cloud services into a company’s technology stack without official authority, either as a workaround or out of necessity.
How does Cloudflare help businesses with multi-cloud management?
Businesses can control the performance and security of their cloud deployments with Cloudflare from a single dashboard.To assist assure performance and security for users everywhere in the world, the Cloudflare network spans 285+ cities throughout the globe.
Solution by F60 Host
F60 Host helps companies create dependable, straightforward-to-manage cloud infrastructures through partnerships with cloud service providers like Jumpcloud.
F60 Host enables businesses to manage the security and performance of their cloud deployments from a single dashboard With Secure directory services, SSO and user lifecycle management, and more.
Follow On LinkedIn
