In-Depth Guide to Shared Hosting
What is Shared Web Hosting?
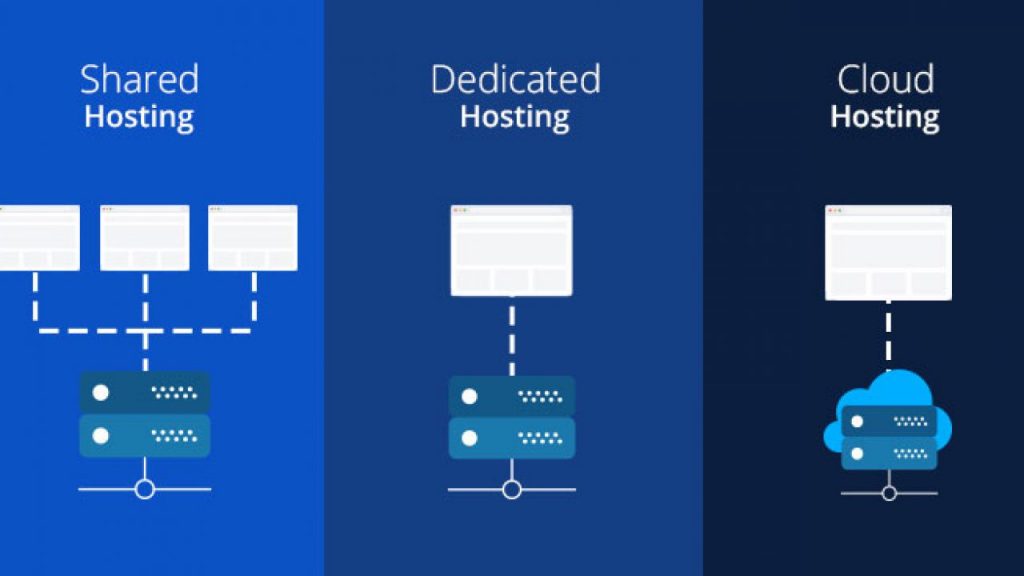
What is shared hosting, and how does it work? Simply put, it’s a hosting arrangement in which several websites share server space.
Hosts may offer reduced costs since you’re sharing space with other accounts, which is why shared hosting is the most popular kind of hosting, especially among newcomers.
In this piece, we’ll go over the basics of shared hosting and help you determine if it’s perfect for you. If that’s the case, we’ll also suggest some of the top shared hostings.
Despite the variety of hosting alternatives available, shared hosting, particularly entry-level hosting, remains the most popular choice for most websites.
Your website shares shared server resources like RAM and CPU with many other customers in addition to server space. This setup saves money on hosting and requires little technological expertise on the part of the users.
However, shared hosting isn’t without its drawbacks: depending on your hosting package, your website may not be able to manage large traffic efficiently, and you may not have root access. The server’s overcrowding may potentially impair the performance of your website.
Entry-level shared hosting plans may be the right economical alternative if you’re beginning a tiny blog with little traffic or simply establishing a new site and don’t know how to host a website.
Other Types of Web Hosting
Shared hosting is one of the most popular ways to get your website up on the internet. But, there are other options too, like:
- Dedicated hosting: Allows you to rent the entire server for your exclusive usage. This results in improved website speed and complete server management. It’s best suited for websites that require a lot of resources. Needless to say, this is not cheap.
- Virtual private server (VPS): Is a great alternative for those looking for a hosting solution that falls between shared and dedicated hosting. It partitions the server into multiple virtual servers, each of which works as if it were its own dedicated server. Users will have root access and will be hosted in a secure environment.
- Managed hosting: Routine administration of hardware, operating systems, and popular applications is handled by certain hosting firms. They handle software installation, configuration, management, upgrading, monitoring, technical assistance, and maintenance, so you can concentrate on your content. In reality, there are organisations that specialise in WordPress hosting (the hosting server is optimised to run WordPress websites only).
- Reseller hosting: If you’re thinking of creating your own hosting firm, this one’s for you. It has a unique control panel for each of your websites that you can use to manage them.
- Cloud hosting: This isn’t technically a different type of hosting; it just refers to a collection of servers (cloud) working together to host a big number of websites. The benefit is that it is extremely scalable, allowing for both huge traffic volumes and abrupt traffic spikes. The majority of charges are based on usage.
What you should look for in shared hosting?
Let’s look at how to choose a decent hosting services provider now that we’ve covered what shared hosting is. It has a significant impact on the security of your data, website performance, and traffic. The following are some of the parameters to look into:
- Storage space – The amount of physical disc space allotted to you for storing databases, files, and other media. It all depends on how big your website is.
- Bandwidth –The maximum quantity of data that your website visitors may upload to/download from it. If you go above this limit, you may have to pay additional fees on top of your plan rates. Despite the fact that most hosting companies provide limitless bandwidth, data transfer rates might suffer if the right infrastructure isn’t in place.
- Uptime – Visitors must be able to access your website at all times. The majority of service providers offer 99 percent uptime, however you should strive for 99.9% or higher. You can check it using uptime monitoring.
- Customer support – This may actually be at the top of the list, especially if you’re new to hosting and don’t have a lot of technical knowledge. Most hosts nowadays provide help 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- Security – Your information must be kept safe and secure. Security measures are frequently omitted from low-cost hosting services.
- Easy to use dashboard – It’s more convenient if the control panel allows you to complete the majority of operations using a user-friendly interface. Pre-installed applications and eCommerce capabilities are also appealing. Examine the dashboard to determine whether it includes any applications that are relevant to your website.
- Database and programming language – The server must be able to handle a wide range of databases (MySQL) and programming languages (PHP). This makes it easier to update to newer technology or switch languages in the future.
- Domain name – Some hosting companies additionally provide domain name registration as an add-on option. This is useful if you want to set up and operate your website from a single location.
Pros and cons of shared hosting
The most obvious benefit of shared hosting is the cost savings. Monthly rates as little as $3 are available. Not only that, but it’s also practical: you won’t have to bother about server upkeep. There’s also the benefit of being able to scale up as needed without having to go into technical intricacies. At the top end, several hosts also offer customizable packages.
What could be negative with so much going for it? For one thing, there’s security. A breach of any one website on the server has the potential to harm all other websites on the server (though some shared hosts implement strong security isolation). Increases in traffic to other websites might cause yours to slow down. Finally, you may have to wait a long period for assistance.
More information:
For more information about Google G Suite/Workspace domains, Server, Hosting, check out these F60 Host resources: