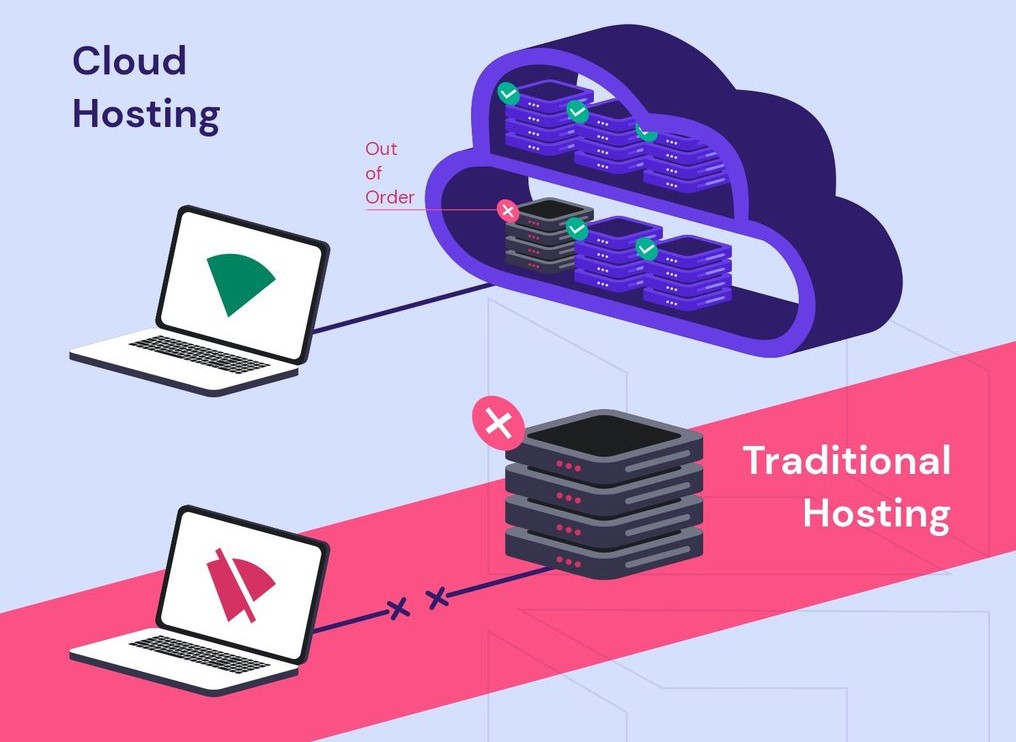
What is Cloud Hosting?

A virtual server is used to host websites in cloud hosting. Traditional web hosting services, on the other hand, often hold one or more websites on a single physical server.
This guide will assist you in determining whether cloud web hosting is a better fit for your needs.
We’ll go over everything you need to know about cloud hosting, from how it works to which types of websites it can help. Then we’ll contrast cloud hosting with other web hosting options.
What Is Cloud Hosting and How Does It Work?
Cloud hosting is a type of hosting that allows a website to take advantage of the resources of numerous servers, resulting in improved performance.
What Are the Different Types of Websites that Use Cloud Hosting?
Virtualization is how cloud hosting works. Cloud servers are a system that divides a real server into numerous virtual ones. These are then linked together to form a single network for hosting a website.
This form of hosting is also known as cluster server hosting because of its interconnected cloud structure.
Is F60 a provider of cloud hosting?
We do, in fact. To provide the best performance, F60’s cloud hosting services use the most up-to-date technologies, such as Cloud Linux with LVE containers to isolate resources for each hosting account.
Here’s a comparison chart of the three cloud hosting providers available to assist you in making your decision:
| Features | Startup | Professional | Enterprise |
| Pricing | 824month | 1,566/month | 5,770/month |
| Number of websites | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Number of email accounts | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Memory | 3 GB | 6 GB | 12 GB |
| SSD storage | 200 GB | 250 GB | 300 GB |
| Number of CPU cores | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Bandwidth | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
What Is the Relationship Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS and Cloud Hosting?
The three forms of cloud-based business models are infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). This means they supply their services through cloud infrastructure.
Let’s have a look at how each model differs.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is an acronym for infrastructure as a service. This sort of company often provides firms with cloud-based computer resources, such as servers and storage, to help them run their operations.
Many businesses are opting for IaaS providers rather than creating their own IT systems, which can be costly and difficult to manage. Cloud services, on the other hand, scale quickly, and organizations just pay for the resources they utilize.
Amazon Web Services, a cloud computing platform that houses Netflix’s movie and series database, is an excellent example of an IaaS corporation.
PaaS stands for the platform as a service, and it refers to organizations that provide cloud-based frameworks for developers to use in the development of apps.
Unlike IaaS, these suppliers will manage the client’s cloud server resources, allowing them to concentrate on their tasks.
Google App Engine is an example of a PaaS platform. Users can construct apps using this service without having to worry about infrastructure administration.
Last but not least, SaaS stands for software as a service. Companies use the cloud to deliver a full-featured program that users may access via a web browser or a mobile application in this business model. A good example of such software is the Google Workspace suite.
Cloud Hosting in the Future?
Small and large businesses are always seeking the best ways to improve their workload and end-user experience.
Cloud hosting is crucial in this regard. Their online business can service clients at any moment because to features like easy scalability, maximum availability, high traffic resilience, and hardware failure resistance.
It’s no surprise, then, that cloud computing adoption is on the rise. In the last year, 61% of businesses have moved their activities to the cloud network. After the transfer, 46% of businesses discovered that their expenses were greatly decreased, indicating that this trend is likely to continue in the future.
A Brief Overview of Cloud Hosting?
To host a single website, cloud web hosting makes use of a virtual network of cloud servers. Traditional hosting, on the other hand, stores one or more websites on a single server.
The main advantage of cloud hosting is its dependability. When one cloud server goes down, other cloud servers can step in to keep the website up and running. Webmasters may scale their hosting resources as needed to anticipate traffic spikes, and it is less prone to hardware failure.
As a result, it is the preferred platform for large-scale projects such as corporate websites, e-commerce storefronts, online marketplaces, and search engines. for more detail, you may follow us on F60 Host.
